When setting up an online business, one of the most important aspects you’ll have to consider is the pricing strategy for your products. The price of your products will determine your profit margins, so it's an essential part of running your own business. However, knowing where to begin and how to create a pricing strategy can be difficult. Since there are several commonly used pricing strategies, it's crucial to choose one that suits you and your eCommerce store. If you're grappling with these decisions, it might be worthwhile to find a professional who can tailor your online store’s design to echo your pricing strategy and brand ethos seamlessly.
After you've started to build your online store, you should definitely take some time to run a pricing analysis and think about appropriate pricing strategies for your business. This article will explore different pricing strategies so you can make an informed decision when conducting a pricing analysis for your online store.
What is a Pricing Strategy?
A pricing strategy refers to the type of analysis and procedure a business will take when determining how to value its products. Using the correct pricing strategy is imperative when it comes to profits.
Around 90% of consumers online will shop around to find the best deal for products, as they have the freedom to do so. This means the price of your products is even more crucial than in a brick-and-mortar store. They only compete with nearby stores, while eCommerce businesses compete with all other online stores.
9 Pricing Strategies You Should Know About
Businesses use many different types of pricing strategies. Some are more popular than others, but they can all be helpful when conducting a price analysis for your store. Let's explore nine of the most popular ones.
Cost-Based Pricing Strategy
Cost-based pricing is the most straightforward pricing strategy. It means calculating production costs and then marking up the price to ensure you make a profit. So if your product costs you $10 to make, and you want to make a $10 profit, you'd put the price at $20. Manufacturing organizations use this model, placing a mark-up on products to ensure they make a profit on every sale.
Cost-based pricing is a popular pricing strategy but comes with its disadvantages. Firstly, it does not consider the consumer and how much they would be willing to pay for your product. It also doesn't consider the current market rate for those products. So while selling each product will make a profit, people might not want to pay.
Market-Based Pricing
When using a market-based pricing strategy, companies consider their competitors’ pricing and the current market rate before setting a price on their products. It involves conducting market research on identical or similar products to gauge what price they sell for.
The calculation is product cost + market price.
Some organizations might add a premium to the price if they think their product is worth the value. This form of pricing strategy is common with smartphone companies. They all look at each other's current pricing before determining their own. Market-based pricing means your prices will be competitive with the current market. But if another organization makes an error with their pricing, you could too. It also doesn't consider customer value, which is a crucial aspect of pricing.
Dynamic Pricing
This pricing method involves the prices constantly changing throughout the day depending on fluctuating demand and market rates. Organizations can use several dynamic pricing tools to calculate this and organize your dynamic pricing strategy for you. Uber uses dynamic pricing. Fares increase with demand and change constantly depending on how many people need a ride. Airline companies also use this pricing strategy for airplane tickets.
A dynamic pricing strategy is helpful because it constantly considers the fluctuating market and maximizes profits with higher demand. Still, it does require constant observation and monitoring as the prices change so regularly.
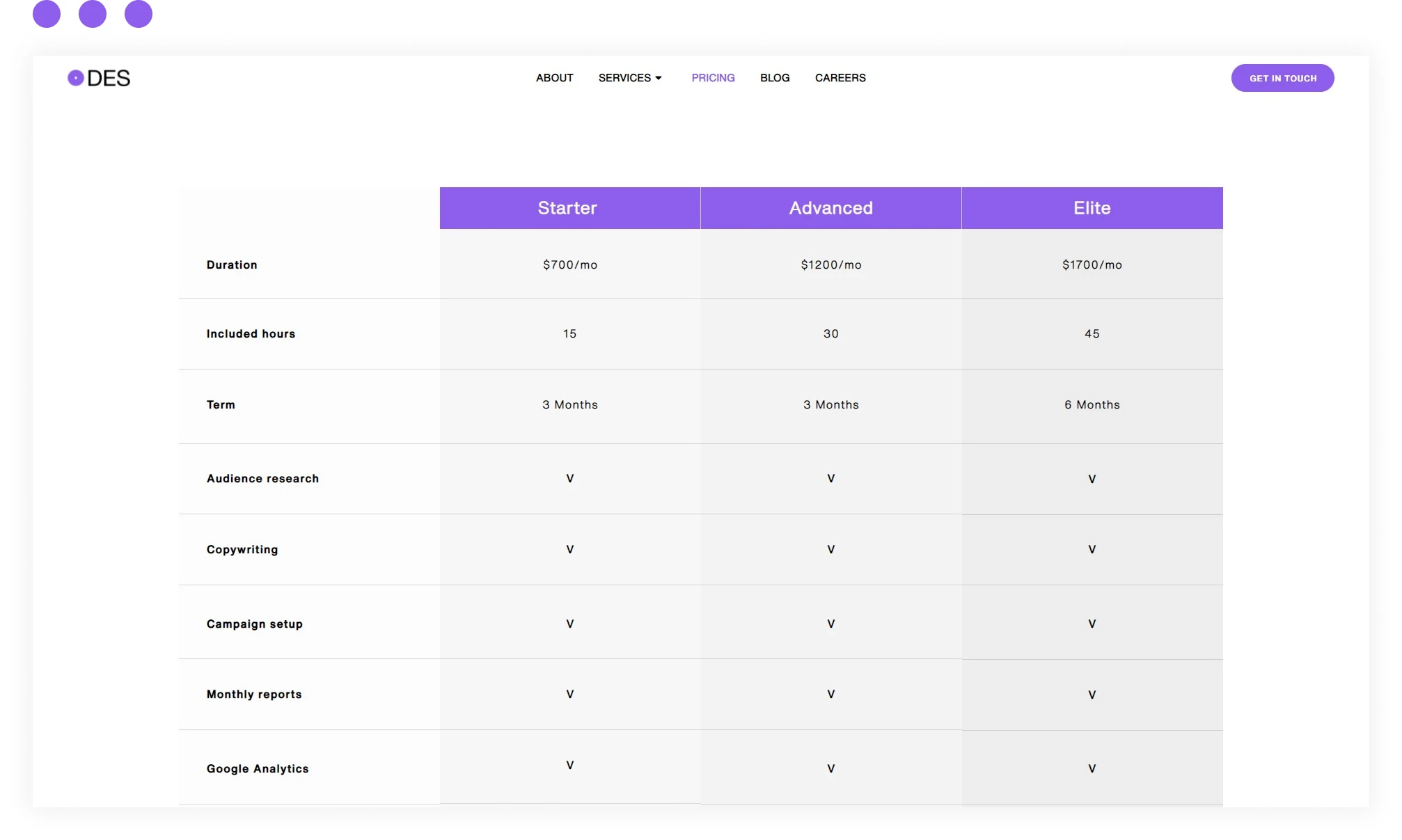
Value-Based Pricing
A value-based pricing strategy involves considering how much value the consumer places on your product and setting a price based on that customer value. Another vital part of this pricing strategy is looking at the current market to see what competitors offer.
One brand that utilizes value-based pricing excellently is Apple. Their products cost more than their competitors, but they've built up a loyal customer base over the years who are happy to pay premium prices for their products.
Value-based pricing allows you to make an informed choice about the price of your product based on both market research and customer value. However, it can involve extensive work and resources to conduct this research and get the price right. In business, time equals money.
Price Skimming
This strategy involves putting a product out at a high price and slowly decreasing it over time. It'll attract high-income shoppers, and then other consumers will purchase the product as you lower the prices.
It can be helpful when keeping up with fast-moving trends where there is much demand for a particular product. It's a common practice used for clothing. Stores will put new clothes up to date with current trends on sale at a higher price, then slowly reduce this before they start making sales as new seasonal trends come in.
Placing a high price on products will help profit margins, but it's essential to ensure you're not pricing yourself out of the market. If you charge too much, then consumers will go elsewhere.
Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing is the opposite of price skimming. The aim here is to start selling your product at a lower price and then slowly increase it as time goes on. Offering a discounted price can help with sales initially and mean you sell more of the product and promote customer loyalty. The point is to charge lower than your competitors to get into the market and hope that customers are happy to pay the full price later.
This strategy is used a lot for subscription-based services. You get the first month free or at a lower price and then pay full price later. When established companies release new products, they'll introduce them to the market at a lower price for customers to try. However, it is a risky choice as it could mean selling your products for less than they're worth at first.
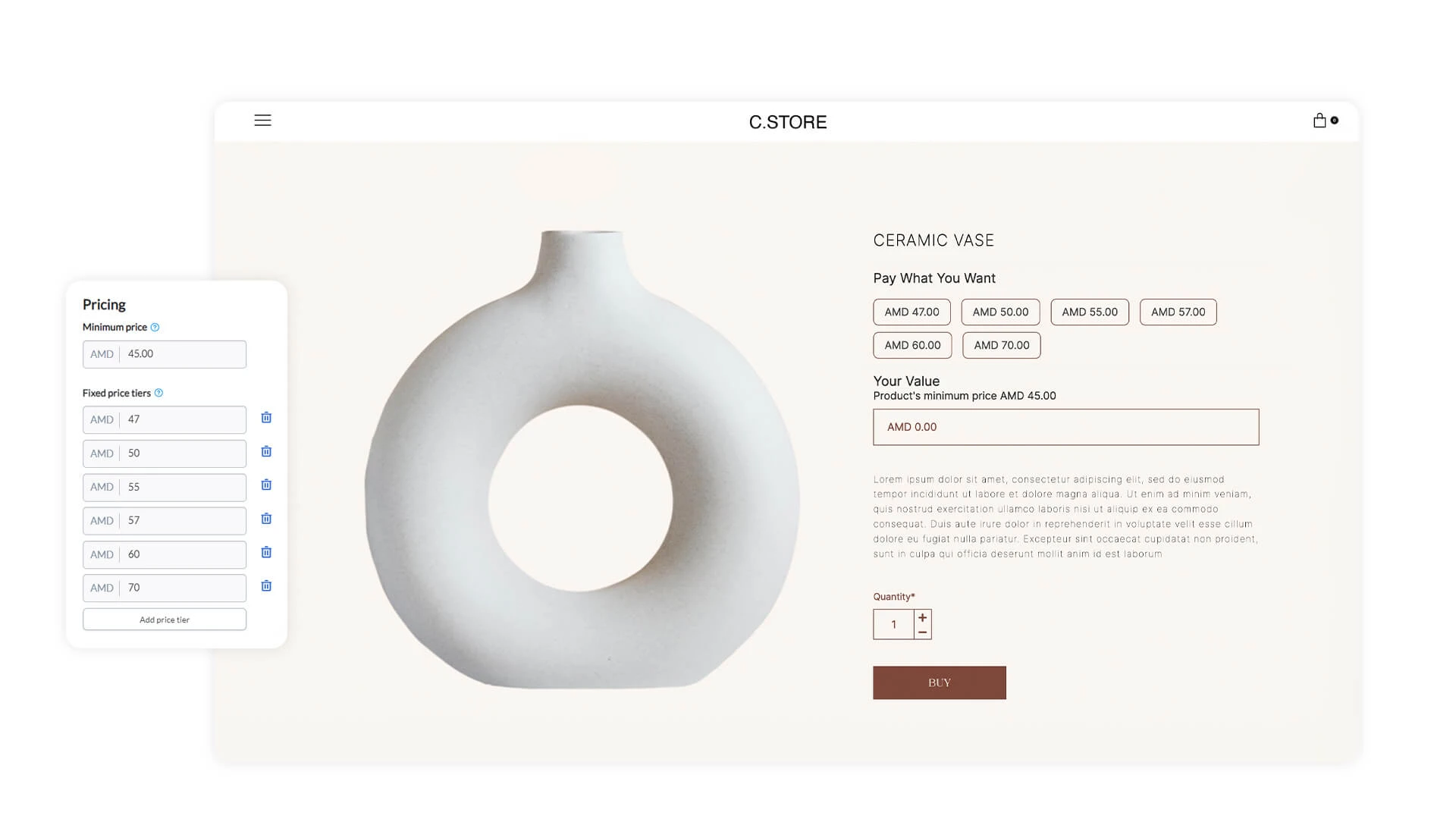
Bundle Pricing
When a company combines two or more products and sells them at a lower price than they would retail individually, this is a bundle pricing strategy. HumbleBundle is a website for this purpose, the website bundles together video games packages. It sells them all at a lower rate than users would pay individually.
It's an excellent pricing strategy in terms of customer value. Consumers are more likely to pay for it if they perceive the bundle as having a higher value than it's selling for. It can also help sell off less popular products by bundling them with higher-value items. Generally, you want to bundle products together that are similar and complement each other.
However, customers might not want all the products in the bundle and, in some cases, may prefer to pay separately. It's vital to ensure that bundle pricing benefits your business and the consumer.
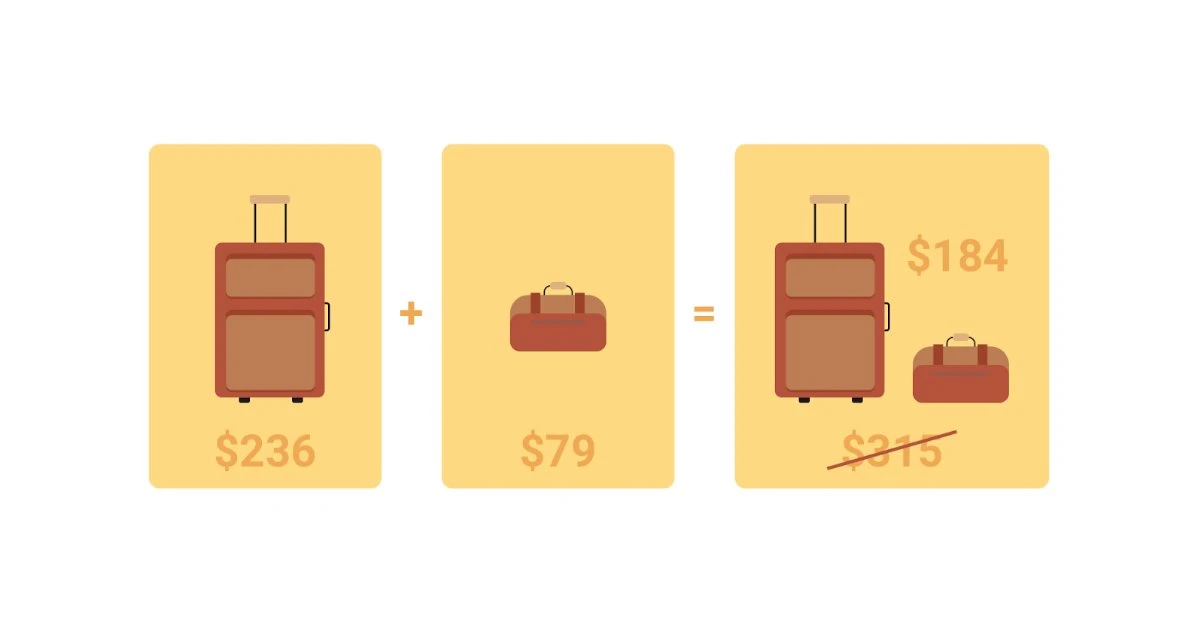
Anchor Pricing Strategy
Anchor pricing is where you use one product as an 'anchor' by placing another more expensive product beside it or putting the product on sale.
For example, you sell apparel, and you want to sell a hoodie for $35. You will be more likely to attract customers by putting it up at $45 and then striking through that price and placing $35 beside it. The customer uses the $45 as the anchor point and thinks they're getting a deal as it's $10 cheaper. You're giving the idea that the product is worth $10 more than you're selling it, giving the customer greater value.
Anchor pricing is an excellent tool when comparing subscription packages. You're showing the more expensive/cheaper options, with the middle package being the 'anchor.' However, it doesn't always work. Customers are becoming wise to this approach. Organizations were outed during Black Friday 2021 as consumers realized they could have purchased the products cheaper at other times.
Loss Leader Pricing
This pricing strategy involves selling products at a loss. Organizations use this when breaking into new markets or drawing in new customers. This is often seen with credit cards offering introductory rates. Or, a company launches a new product and initially sells it at half price to entice customers to try it.
It is a controversial pricing strategy, especially as there's no guarantee a customer will continue to buy the product when it goes up to the full price. Coming in at a lower price point could set the customer value low, meaning consumers will be put off when you change the cost to the total amount.
How to Choose a Pricing Strategy
Now that you've read about the variety of pricing strategies available on the market, you might be wondering how to choose the best pricing strategy for your business. Learning how to conduct a pricing analysis, then, is pivotal to the success of your brand. However, there are several factors to consider when conducting a pricing analysis, like:
• Your target market and how much they will be willing to spend;
• The costs to your business for manufacturing;
• What prices competitors are currently selling at;
• The customer value of your product.
Ultimately, your business needs to be profitable to succeed. Considering all the above options should help with your pricing strategy deliberation. Remember, no pricing strategy needs to be forever. You can try one and then another. Your pricing strategies may vary depending on what different products you have. Testing pricing strategies and changing them over time will help you find the right one for your business. Some website builders, including Ucraft, offer valuable integrations for data tracking and analytics to help you determine what pricing strategies are working.
Verdict
There are many different pricing strategies, each being valuable for specific industries, markets, and store sizes. Choosing the right pricing strategy for your business will require research and consideration of your consumer base, target market, customer value, and products.
You don't have to stick to the same pricing strategy for every product, and you can test and change options based on these factors. Once you build up a loyal customer base for your brand, it will be easier to determine pricing strategies for your products. But taking the time before launching your online store to select a pricing strategy is crucial to the success of your business.
Once you've figured out your pricing strategy, all you need to do is build your website! Ucraft offers a wide variety of eCommerce templates for any industry, so choose one that suits your store or business idea and get started.

